Solar systems are designed to make use of the sun’s energy to heat water or air for different purposes, both in residential and commercial settings. There are two main types of solar thermal systems: active and passive. Active systems require the use of pumps, valves, and controllers to circulate the heat transfer fluid, whereas passive systems use natural convection or thermosiphon to move the fluid.
Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, which depend on factors such as climate, design, and cost considerations. This article aims to explore the key benefits and drawbacks of active and passive solar thermal systems, providing readers with the necessary information to make an informed decision when choosing the most suitable option for their specific needs.
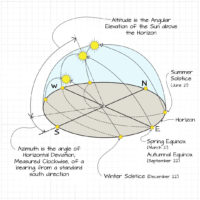
What Is Solar Energy?
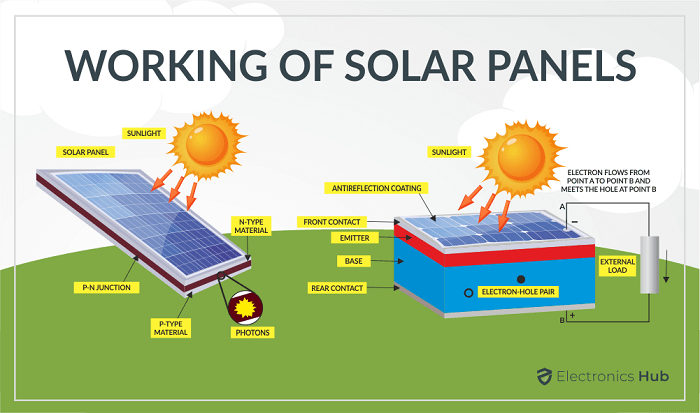
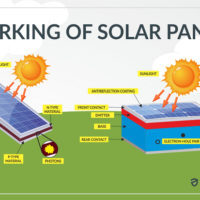
In simpler terms, solar energy is the process of converting the energy emitted by the sun into usable electricity, which can then be used in homes, businesses, and other settings. The sun is a powerful source of energy that emits photons, which can be captured and converted into electricity using solar panels.
Why Is Solar Energy Important?
Solar energy is a highly clean and easily available source of power. It is fascinating to note that the sun emits more energy in an hour than the entire human population consumes in a year. By harnessing this abundant energy in an efficient way, we can minimize our dependence on polluting fossil fuels and other harmful energy sources, which will help in safeguarding our planet.
The Difference Between and Passive Solar Systems
Solar energy systems come in two types: passive and active. Although both systems convert solar energy into electricity, they differ in terms of their setup and operation. While both systems provide heating benefits, certain types of buildings are better suited for one system over the other. Passive systems rely on the sun’s heat, while active systems only require solar irradiance to function. This difference in operation has implications for your specific needs. To understand this further, let’s explore each system’s advantages and disadvantages.
Passive Solar Systems:
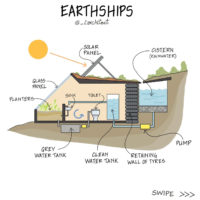
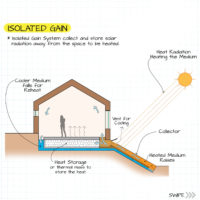
Passive solar energy is a system that collects and stores solar heat without using any external devices. It uses thermodynamics to convert solar heat into power. This method is particularly effective for heating and cooling systems, especially in small homes. However, it may not work as well in areas with rainy or cloudy weather. On the other hand, active solar systems use hot water pumps or fans to circulate fluids.
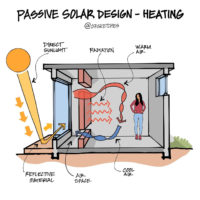
One of the main advantages of active systems is that they enhance the efficiency of your solar system. Active solar panels rely solely on external energy sources. In contrast, passive solar energy uses special windows placed on the south-facing side of buildings to capture solar heat. Some systems may also incorporate PV panels, but that combines both active and passive solar methods. The redistribution of heat through the area ensures even heating, as heat naturally moves from warm areas to cooler ones, utilizing thermodynamics.
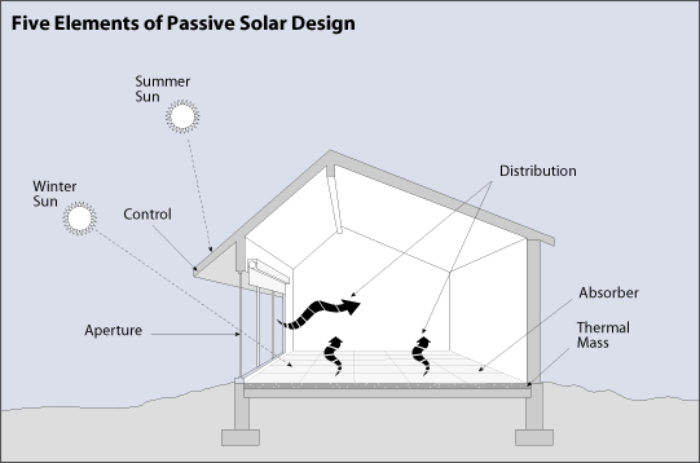
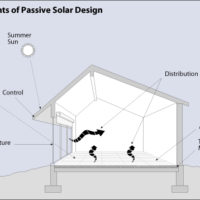
Passive Solar Design Basics
Passive Solar Heating
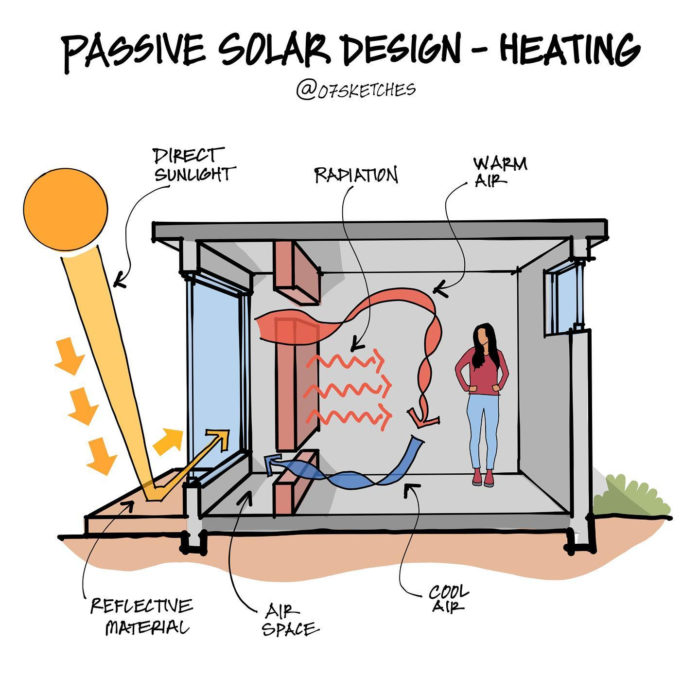
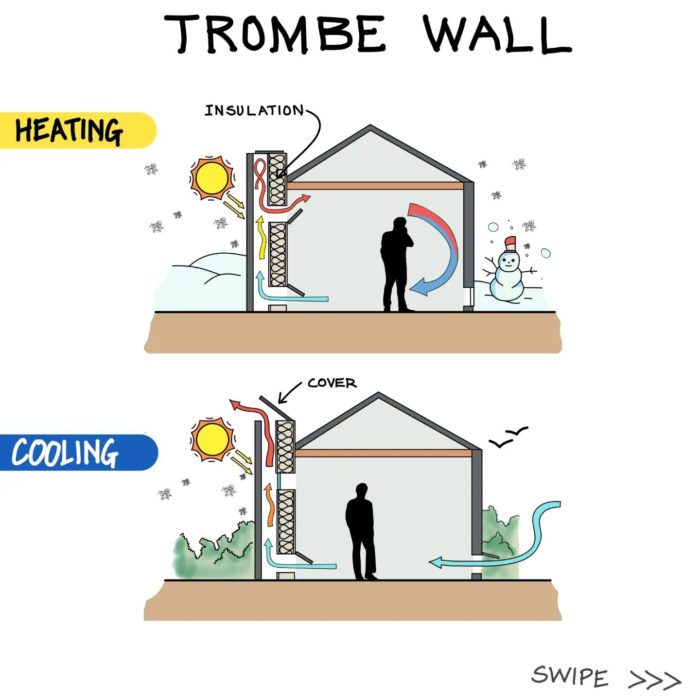
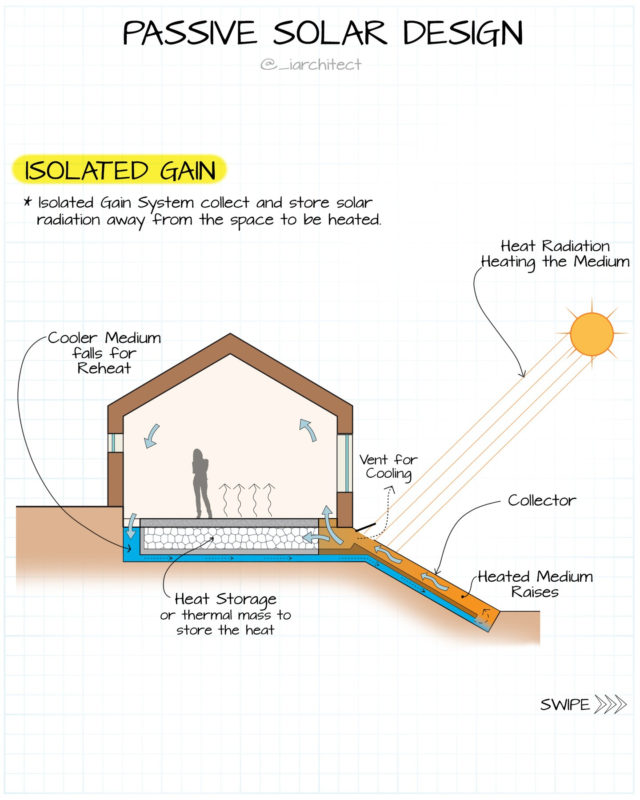
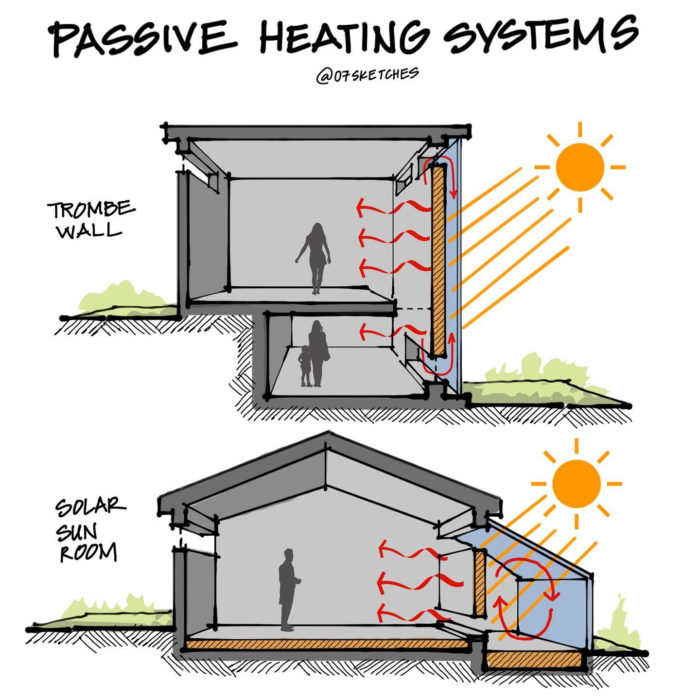
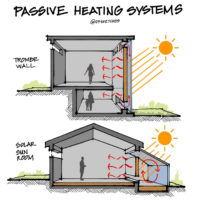
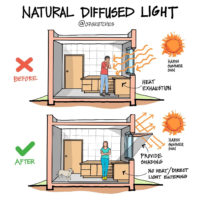
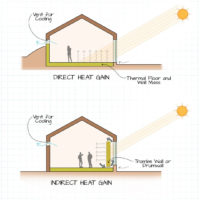
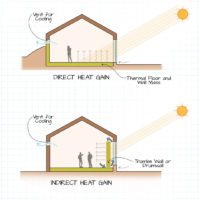
Passive solar heating systems aim to capture the heat of the sun and use it to warm up a building. This is achieved by incorporating south-facing glass to capture sunlight and thermal mass to absorb, store, and distribute the heat. There are several methods to implement these elements, such as Direct Gain and Indirect Gain.
Passive Solar Cooling
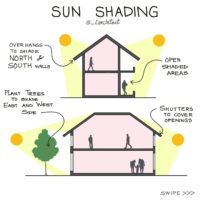
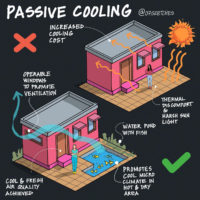
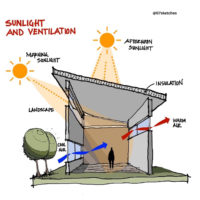
Passive solar cooling systems function by minimizing heat gain during the day, promoting natural ventilation, exchanging warmer indoor air with cooler outdoor air whenever possible, and utilizing the coolness of the night to regulate warmer daytime temperatures. Simple passive solar cooling systems incorporate features like overhangs or shades on south-facing windows, shade trees, thermal mass, and cross ventilation. These elements, including shading, thermal mass, ventilation, and convective cooling, all contribute to the effectiveness of passive solar cooling systems.
Advantages Of Passive Solar Systems
Passive solar thermal systems offer several advantages over active systems. They are more economical and simpler than active systems, requiring fewer components and no electricity. They also have lower maintenance requirements and a longer lifespan, as there is less wear and tear and fewer points of failure. Passive systems can be more aesthetically pleasing and less intrusive, as they can blend in with the building’s roof or façade.
They are particularly suitable for single-family or rural homes with lower and more stable hot water or space heating demands. No external equipment is required, making the entire setup cost-effective. Passive solar energy is free to use and does not cause allergies or dry out mucous membranes, making it beneficial for one’s health. Overall, passive solar heating is an ideal solution for smaller homes and offices.
Disadvantages Of Passive Solar Systems:
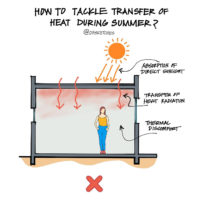
Passive solar thermal systems have some drawbacks when compared to active systems. They are less efficient and versatile because they cannot control or optimize the heat transfer process. Additionally, they have lower storage capacity and heat loss protection, which can limit their performance and availability. Passive systems are also vulnerable to freezing or overheating, which can damage the components and reduce the system’s lifespan. Furthermore, careful design and installation are required as these systems depend on factors such as orientation, slope, and location of the collector and tank.
Passive solar heating is dependent on the type, design, and placement of windows, as well as the mass/material of walls and floors. Overheating can be a problem in extremely hot climates, while in colder climates, passive solar heating systems may not produce enough heat in the winter. The efficiency of these systems is directly dependent on the weather, and in hot areas, there is a potential for overheating. It is therefore important to choose the right kind of windows to maximize the success of the system.
Active Solar Systems
Active solar systems utilize pumps or fans to move fluids and increase the efficiency of solar systems. Active solar energy is commonly used in solar panels and can be employed for heating and electricity to power homes and communities. The process involves capturing the sun’s heat using either air or liquid, which is then converted to energy and stored. Liquid is a better conductor of heat and energy, while air does not freeze. Both fluids can be used for heating and cooling purposes, with liquid collectors known as hydronic collectors and air systems known as air collectors.
Active Solar Space Heating
Active solar space heating is a method that uses mechanical equipment such as fans, pumps, blowers, and ducts to collect, store, and distribute heat within our homes. There are two types of active solar systems: liquid-based and air-based. In liquid-based systems, large water tanks are used to store and distribute the heat, and pumps, radiant slabs, central forced air, or hot-water baseboards are employed. On the other hand, air-based systems use thermal mass or rock bins to hold the heat, along with ducts and blowers to distribute it. Overall, active solar space heating systems are an efficient and effective way to keep your home warm while saving energy.
Active Solar Water Heating
Active solar water heating systems are a popular way to heat water in homes. These systems use pumps to circulate water or a heat-transfer fluid through the system. There are two types of active solar water heating systems: indirect and direct. In the indirect system, an anti-freezing mixture is used to heat a fluid in the collector, which is then transferred to a storage tank. A heat-exchanger then transfers the heat from the fluid to the household water. In direct systems, the household water is heated directly in the solar collectors. Once the water is heated, it is pumped into storage tanks and then piped into faucets for use.
Advantages Of Active Solar Systems
Disadvantages Of Active Solar Systems
Passive solar thermal systems are generally more affordable and straightforward to install compared to active systems. This is because active systems require more components and wiring, which makes them more complex and expensive. Additionally, active systems use more electricity to operate, which can offset their energy savings and environmental benefits. Moreover, active systems are more prone to leaks, noise, and malfunctioning, which can negatively affect their performance and safety.
Regular maintenance and inspection are required for active systems, which can increase their operational costs and inconvenience. Furthermore, the initial cost of an active solar heating system is higher than that of a passive system, and equipment maintenance is also more costly. It is also important to note that the fluids used in the solar panels for heat storage have the potential to release toxins into the air.
- © ELECTRONICS HUB
- Snøhetta
- © Hervé Abbadie and Karawitz
- © Greg Premru
- © EERE
- © _iarchitect
- © 07 sketches
- © 07 sketches
- © 07 sketches
- © 07 sketches
- © 07 sketches
- © _iarchitect
- © _iarchitect
- © 07 sketches
- © _iarchitect
- © 07 sketches