Pushed Slab
The Pushed Slab is located between two completely different urban grids: the dense city fabric of blocks and streets in North Paris and the loose urban fabric in the south with its clear defined and straight forward infrastructure. The design is based on the requested office program and energy requirements. The project combines proven energy efficiency technologies with individual office floors and outside spaces such as patios, balconies and a garden. The building is highly flexible offering three cores and a central lobby. It can be rented out to one or various tenants without structural changes.
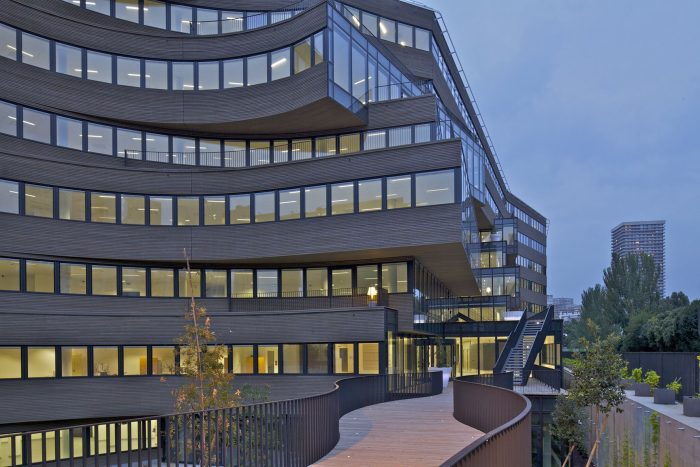
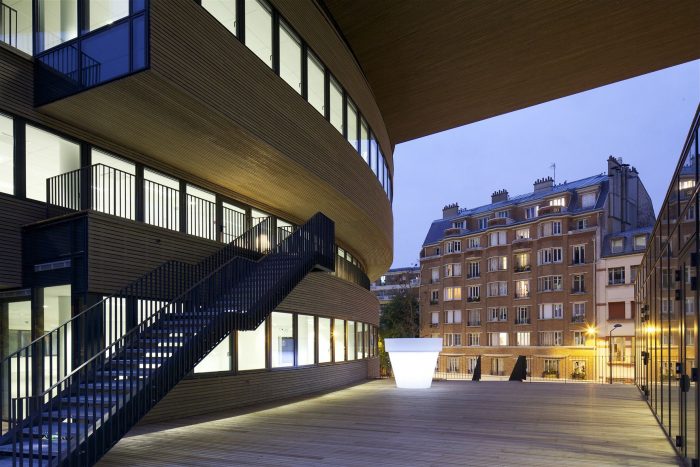
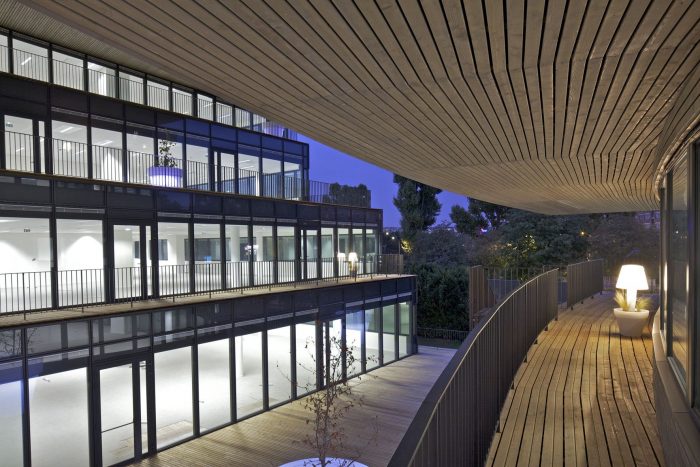
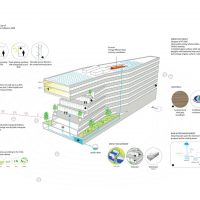
The building is located on a former rail embankment of approximately 4,000 square meters. The volume follows the site restrictions, a slab shaped volume of 150 meters long and 21 meters wide. An opening in the volume preserves the view of a historic building. To create this urban window and to enhance the urban quality of the neighborhood, the slab is ‘pushed’ until it breaks, then twisted and pushed to the south. This pushing act creates a distortion of the floors, offering multiple terraces which can be directly accessed from the work areas as well as from the external staircases. The urban window offers a large terrace on the second level. The terrace and the balconies are furnished with trees planted in large pots, offering employees a friendly environment to relax.
The building is wrapped in a skin of wood. The windows form a rhythmic ribbon, offering optimal sun and light control of the inner spaces. To contribute to the sustainable development and taking the impact of deforestation into account, FSC certified wood is used.
MVRDV specifically designed the eco-office building to achieve a high level of energy efficiency and sustainability. 264 photovoltaic panels placed on the roof will generate 90 MW/year and a grey water circuit will be applied. 22 solar thermal collectors will generate 45% of the energy needed to heat the water. Sun blinds are integrated in the south facade and in the cuts. The building is insulated from the outside in order to reduce thermal bridges. The accumulation of these proven reliable techniques results in a highly efficient low-energy building which leads to an energy consumption of 46 kWh per m²/year achieving a BBC Effinergie energy label and complying with the objectives set out in the ‘Plan Climat de la ville de Paris’.
Winy Maas, principal architect and co-founder of MVRDV says, “Pushed Slab is an exemplary combination of high energy efficiency, economic reality and architectural quality. This emerged from an ambitious client, ICADE, and a city with a long term vision. The added demand of a preserved view line gave the project its exciting shape, it now respects the surrounding neighbors and it opens up its heart for a collective meaning“.
Project Information :
Architect : MVRDV
Location : Paris, France
Project Year : 2014
Total Area : 19,000 square meters
Co-Architect : North by North West, Paris, FR
Design Team : Winy Maas, Jacob van Rijs and Nathalie de Vries with Frans de Witte, Bertrand Schippan, Catherine Drieux, Victor Perez, Delphine Borg, Billy Guidoni
Structure : Terrel, Paris, FR
- photography by © Philippe Ruault
- photography by © Philippe Ruault
- photography by © Philippe Ruault
- photography by © Philippe Ruault
- photography by © Philippe Ruault
- photography by © Philippe Ruault
- photography by © Philippe Ruault
- photography by © Philippe Ruault
- Diagram
- Model