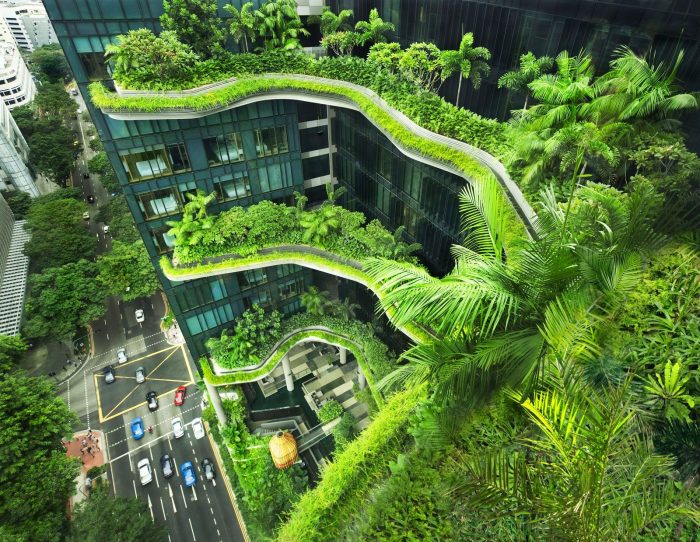
Sustainable buildings are a broad and growing field with many unique properties. The term refers to architecture sensitive to natural landscape features, local context, user needs, and sustainable development.
In other words, sustainable architectural buildings are environmentally friendly and take into account every step of the planning and building process, from selecting building materials to designing and implementing heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and cooling systems to incorporating the built environment with the environmental conditions.
Sustainable Architecture definition
Sustainable development can be defined as tackling present needs without compromising future generations’ ability to handle their requirements, according to the World Commission on Environment and Development. When we apply this delicate idea to architecture, it refers to creating healthy living spaces while aiming to reduce harmful effects on the environment, energy use, and human resources.
A building’s materials, construction techniques, resource usage, and overall design all demonstrate sustainable architecture. Additionally, the plan must enable sustainable operation throughout the entire building life cycle, including final demolition. Although it must be aesthetically pleasing and functional, constructors and architects must put in mind while planning and building to achieve long-term energy and resource efficiency.
Green architecture or environmental architecture are other names for sustainable architecture. It pressures architects to create sophisticated plans and make the best use of available technology to ensure that buildings have an as little negative impact on the ecosystem.
What is the concept of sustainable buildings?
In their research, GREEN ARCHITECTURE: A CONCEPT OF SUSTAINABILITY, Amany Ragheb, Ghada Ragheb, and Hisham-El Shimy suggested that understanding the site in all its beauty and complexity is the first step in the design of a green building. An ecological design strategy aims to incorporate new systems with natural environmental processes already taking place in the area. These ecological processes purify the air, create ecosystems, respond to the sun’s movements, and capture, filter, and store water. There are also plenty of free resources discussing sustainable architecture and design books, only if you’re a geek and fan of architecture books.
Some researchers propose that the project’s sustainability should be a necessity, not only a characteristic, which has been that way since the building of the Ancient Egyptian pyramids and other examples we’ll discuss below in some developing materials where architects, designers, and constructed aim to use specific materials that produce the least negative effect on our environment.
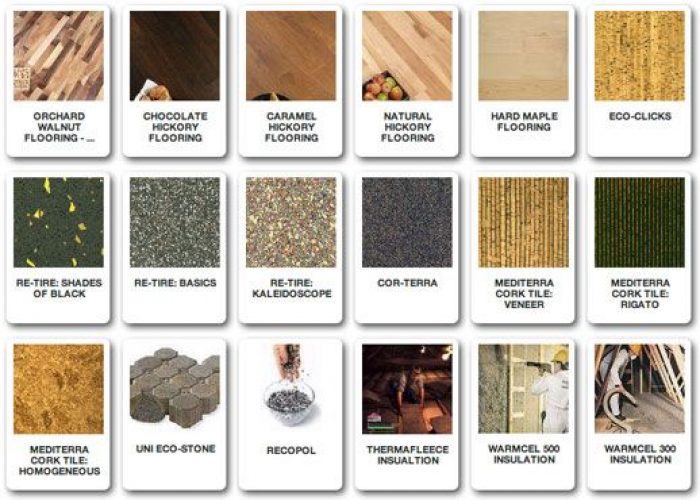
Most Used Sustainable buildings materials
It comes as no surprise that sustainable or green building materials must be durable, recyclable, or both. Recyclable materials must originate from local resources in the region where construction will occur. It’s always better if natural materials such as soil, adobe, wood, cork, bamboo, straw, and sawdust are raw, and the materials shouldn’t be harmed by cold, heat, or humidity conditions. Here are some infamous sustainable buildings materials.
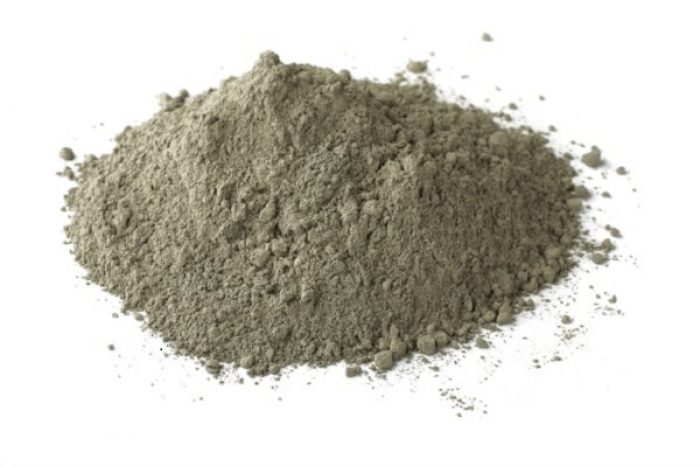
1)Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC):
Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) is a type of typical Portland cement (OPC) that contains pozzolanic materials known to strengthen the concrete’s durability while reducing the amount of cement used. PPC has many benefits over OPC, including lower cost, higher final resilience, less impermeability, etc. Since most large corporations now manufacture PPC instead of OPC, PPC has become the most widely used environmentally friendly material.
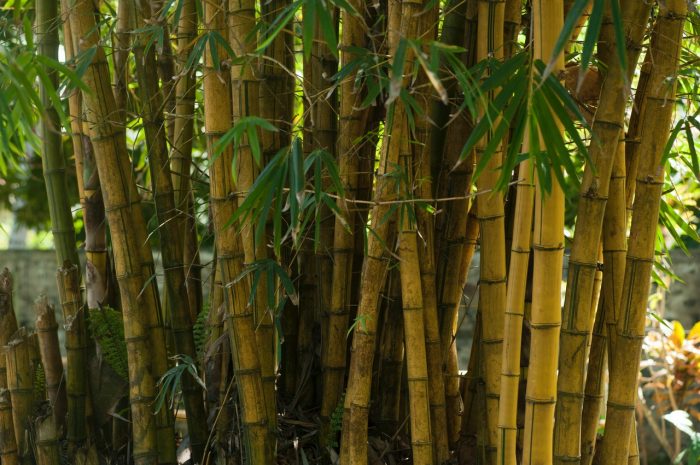
2) Bamboo
Bamboo is a grass that overgrows and has a wood-like aesthetic. Because natural wood is becoming increasingly limited due to the 50-100 years they take to mature; unlike bamboo, which only takes 3-5 years, bamboo has become increasingly popular as a building material.
Bamboo grass stands out because it is five times stronger than concrete and lighter than steel. It is well-suited to resisting moisture and is simple to finish, so it won’t scratch. They can also be replanted and reforested rapidly, making them a dependant, eco-friendly building material.
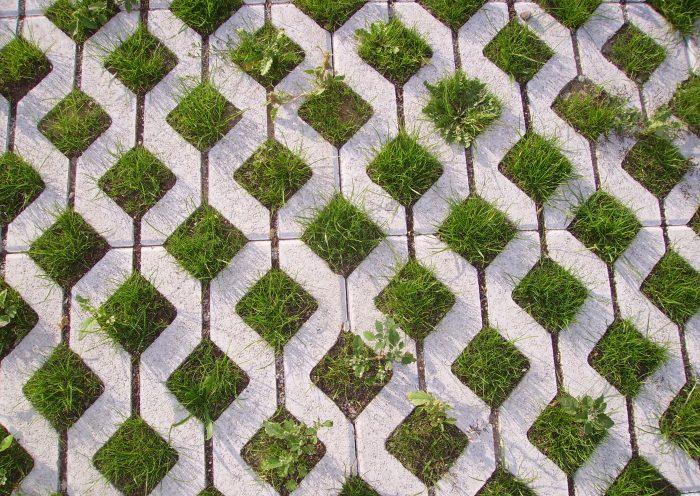
3) Grass pavers
Grass pavers have many advantages over concrete pavers. They offer a more beautiful, natural environment. They assist in water harvesting because they are permeable to water, which concrete pavers do not do. Because they are less expensive, grass pavers are frequently used in landscape gardens, sideways, and walking paths.
4) Plant-Based Polyurethane
Due to the polymer networks’ reliance on heat-insensitive chemical bonds, traditional polyurethane cannot be recycled. However, more recent plant-based replacements provide greater sustainability.
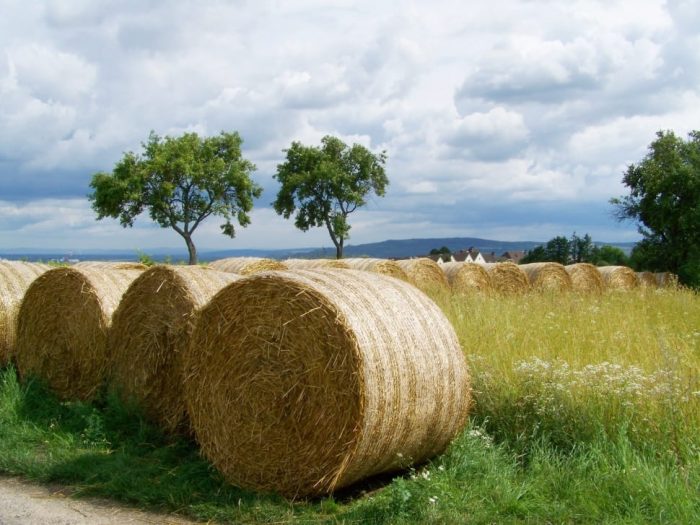
5) Straw Bales
Straw is a renewable resource that can be harvested and replanted with little environmental harm. Straw bales contribute to rising carbon emissions; however, by converting these waste toxins into the compressed ceiling and wall panels, their carbon content is preserved in the most environmentally friendly manner.
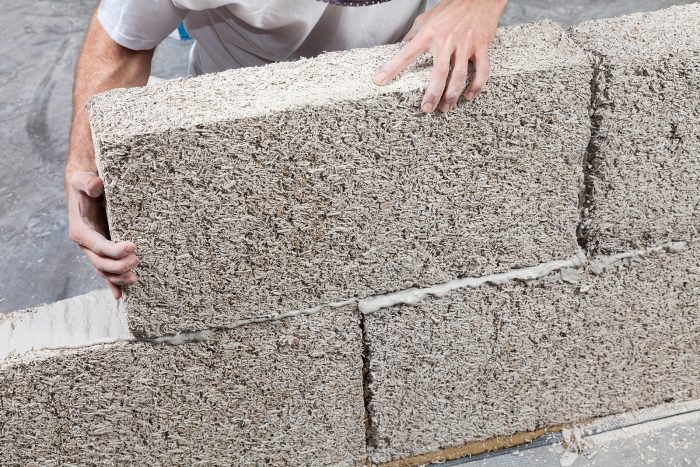
6) Hempcrete
Sand, hemp fibers, and lime are combined to make hempcrete. Typically, it is employed in construction and insulation, and Hempcrete blocks are incredibly lightweight and easy to work with. Hemp is a rapidly expanding renewable resource, so hempcrete is excellent for the environment.
Hempcrete stands out because it is a breathable material that doesn’t shrink, which means that once it has dried, there won’t be any crack lines. Hempcrete may not be as strong as concrete, but it is pest- and fire-resistant and acts as a good insulator.
7) Timbercrete
Sawdust and concrete are combined to create Timbercrete, a sustainable building material. Timbercrete is green because sawdust replaces the concrete’s most energy-intensive components, reducing the material’s carbon footprint. Since it is lighter than concrete or clay, transporting it is much simpler.
Sustainable Architecture examples
Environmentally friendly or sustainably constructed buildings have become more prominent in recent decades. We’ve put together a list of our top Sustainable Architecture examples from around the globe that incorporate sustainable design and original concepts. If by any means, you didn’t feel fulfilled after these outstanding designs, you could still check our list of Sustainable Architecture and Design to Inspire You.
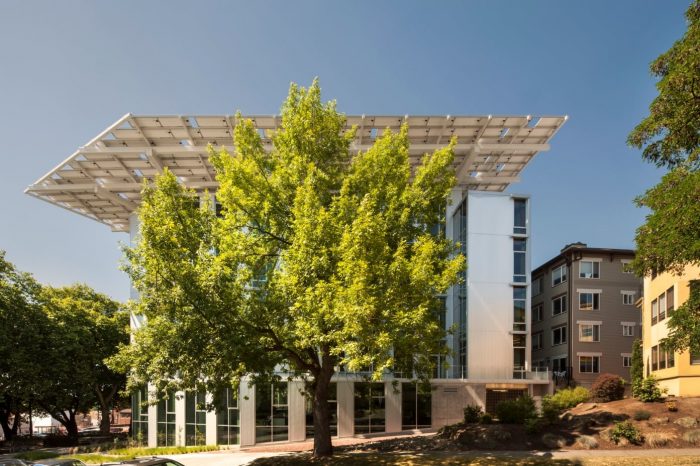
1) Bullitt Center, Washington, United States Of America
This office in Seattle, Washington, was officially launched on Earth Day in 2013 and is well-known for being a zero-energy structure. The 575 solar panels that produce more energy than it needs in a year completely cover their total energy consumption.
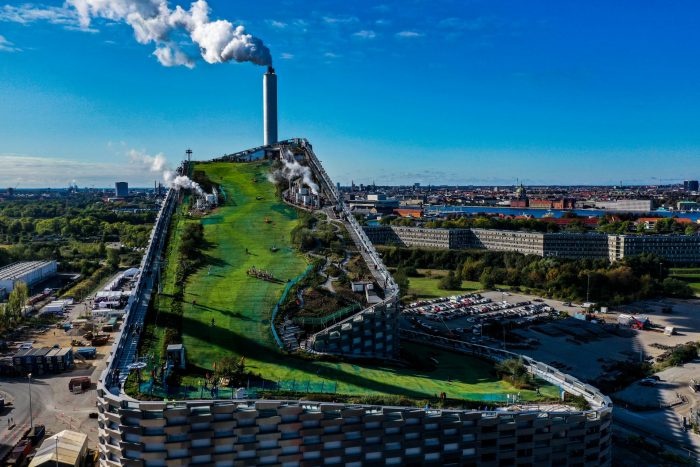
2) CopenHill, København, Denmark
The eco-friendly power plant CopenHill burns waste to produce electricity. The 16,000 sqm structure intends to transform 400,000 tons of waste annually into enormous amounts of clean energy, sufficient to power over 100,000 homes in the area while transmitting no toxins to the benefit of the environment.
3) Eden Project Cornwall, United Kingdom
The Eden Project is a massive public attraction located in Cornwall, United Kingdom, intending to improve everyone’s quality of life. This Nicholas Grimshaw-designed facility tucked away in a sizable crater, comprises two enormous enclosures with thousands of plant species housed nearby domes representing a rainforest and a Mediterranean environment.
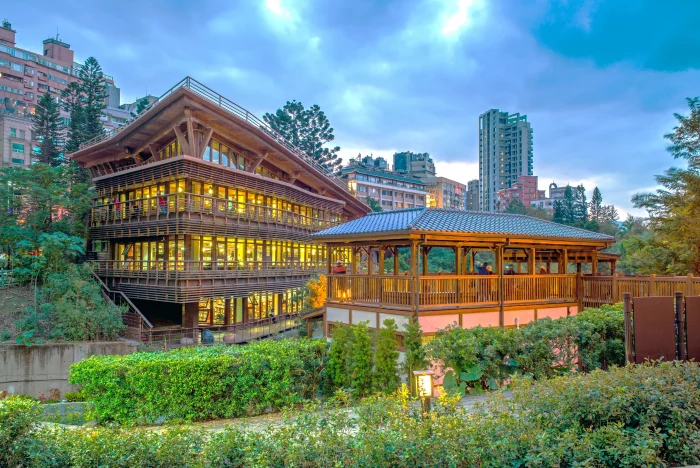
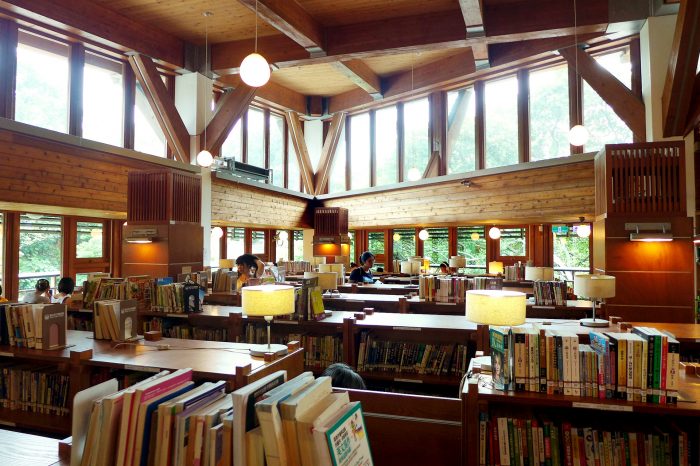
4) Beitou Public Library, Taipei, Taiwan
When nature meets books, the result is Beitou Public Library, Taiwan’s first green library close to the Beitou Hot Spring Park. The structure comprises solar panels with a 16W maximum power storage capacity and a rainwater collection mechanism for flushing toilets and watering indoor plants. The wooden balcony ledge, its most notable feature, saves energy by limiting the heat-producing sunlight that enters the rooms.
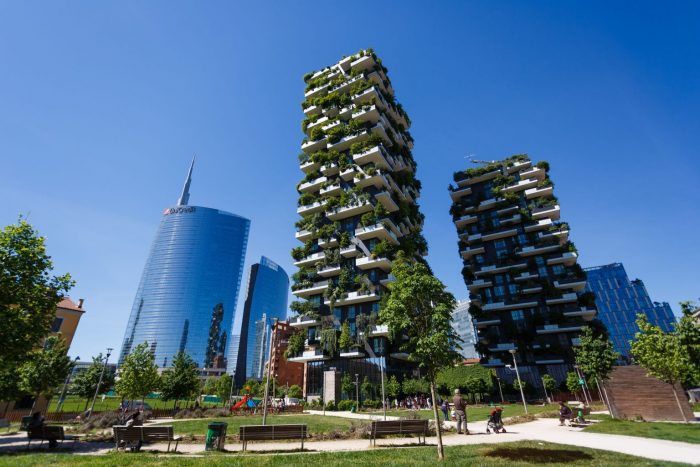
5) Vertical Forest, Milan, Italy
Contrary to structures made of materials like steel or glass, the Vertical Forest residential structure has a facade made of plants that, instead of reflecting sunlight, filters it by regulating the humidity inside the building to create a comfortable temperate climate that doesn’t harm the environment.
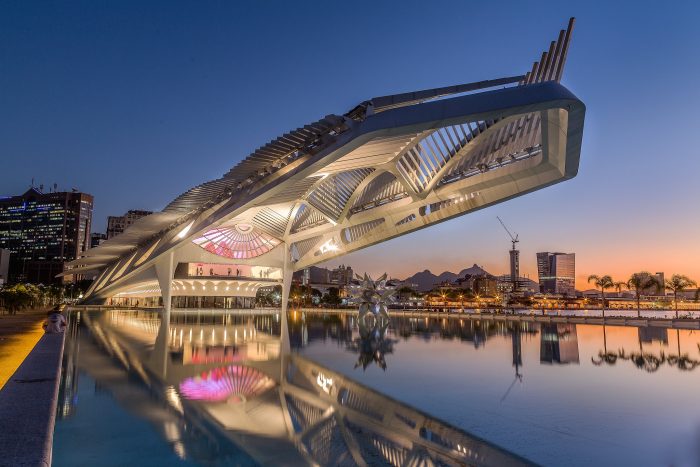
6) Museum of Tomorrow, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
A few of the structure’s sustainability features include mobile PV solar panels that can be adjusted according to the sun’s rays throughout the day and channeling water from Guanabara bay to provide water for the Museum’s enclosing reflecting pools and regulate the building’s temperature.
How do you create sustainable architecture?
All of these past examples show despite being different in many aspects, all share standard regulations which help in improving our ecosystem infrastructure massively. Here, you’ll find some of our essential architectural ideas about sustainability to consider when designing or constructing a new structure.
1) Install Renewable Energy Systems:
Architects can install solar, wind, and geothermal programs for residential properties to reduce their carbon footprints. Architects can reduce building reliance on the traditional grid if solar panels are installed on the roof.
2) Use Low-Impact Building Materials:
By using the green building materials mentioned earlier, contractors can effectively reduce pollution associated with construction. As these materials minimize mold growth, they help protect the environment and the health of residents. To reduce a building’s carbon footprint, contractors may use additional recycled materials.
3) Native Landscaping:
Sustainability isn’t all about efficient water heaters and low-impact- specifications. Often it’s about reminding people of the natural beauty in their surrounding landscapes. For example, landscaping decisions can significantly influence water consumption in public buildings, and architects can dramatically reduce irrigation requirements by utilizing local trees, plants, and grasses.
4) Stormwater Management:
The damaging effects of buildings on the environment can be significantly reduced by implementing stormwater management techniques, such as pavement layer, that aid in reducing runoff and gradually releasing water back into the ground.
5) Low-Maintenance Exterior Sidings:
Durability is the key to sustainability. Making sure a building will last for the next 100 years is the most eco-friendly action you can take when designing. Over a few decades, this lowers waste and energy costs and has the potential to have a significant long-term impact on ecological sustainability.
FAQs:
What do sustainable architects do?
Basically, the architect's role in this situation is to maintain, enhance, and produce high-quality built environments under predetermined circumstances. Architects need to understand that they are members of their environments and are responsible for making those environments more sustainable.
What is modern sustainable architecture?
Modern sustainable architecture is a branch of architecture focusing on the built environment. It involves making choices regarding the construction's materials, energy consumption, and location to minimize the building's adverse environmental effects.
Why is sustainable architecture important?
Sustainable structures are created to lessen their harmful effects on the environment and public health during and after construction. This is accomplished by preserving and protecting the natural surroundings around the project site.
What is the difference between green architecture and sustainable architecture?
The primary distinction between green architecture and sustainable architecture is that Sustainable buildings function with consideration for all three aspects of sustainability (people, planet, and earnings), while green buildings only have the environment as their primary concern.